
What is PPC? Pay-Per-Click Marketing
Of the many digital marketing-related acronyms (SEO, SEM, CRO, etc.), PPC may be one of the most common. PPC stands for pay per click, referring to a type of paid search advertising employed by companies everywhere.
PPC marketing is a popular method that drives traffic, leads, and conversions. We’ll go through the basics of pay-per-click marketing.
PPC Definition
PPC, pay-per-click, is exactly what it sounds like: this method of advertising costs the advertiser a certain amount of money each time their ad is clicked by a potential customer. This is essentially paid search traffic, as opposed to organically grown traffic through SEO.
PPC is mostly done through search engine advertising, namely Google and Bing ads. When you see the first results on search engines like Google with the “Ad” bubble, those ads are search engine advertisements most likely paid for through PPC. Advertisers only have to pay for each time their ad is actually clicked, not each time that it appears on a search engine results page.
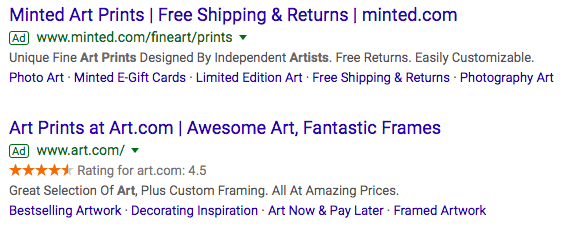
Pay Per Click Advertising
So how much is the cost of pay-per-click ads? Not all PPC ads are equal – some are more or less expensive, depending on factors like your ad’s relevance, the targeted keywords, audience targeting, and more. Each campaign has a different cost per click (CPC) depending on the ad and its targeting.
When running PPC ads, advertisers bid a certain amount they are willing to pay per click or bid a certain amount for an entire campaign over a certain period of time. If their ad is chosen for the search engine placement they bid for, they are then charged a specific fee each time their ad is clicked.
If a PPC campaign is being run correctly, the cost per click will be worth paying, because the visit to your website should be worth more in potential customer leads or future conversions.
Search engines like Google recognize relevant, high quality ad campaigns and reward them with a lower cost per click. This means that a good PPC campaign will be effective in targeting relevant new potential customers and will be cost-effective because it will have a low CPC and yield worthwhile conversions.
Improving PPC ads takes knowledge and testing. It involves finding the best PPC keywords, organizing keywords into ad groups and campaigns, setting up PPC and CRO optimized landing pages, targeting the right audience, and creating high quality advertisements.
Google Pay Per Click Ads
Since Google is by far the most commonly used search engine, it is also the most popular for PPC ads. Google Ads are created in a pay-per-click model, where advertisers can pay to have their ads appear before Google search results and on other Google-owned properties.
Google ads are selected based on Ad Rank, which measures CPC and Quality Score. CPC, cost per click, means that the Google favors the highest bid per click. Quality Score is a metric determined by Google that judges your ad based on its relevance, click-through rate, landing page quality, and more. Based on these two factors of Ad Rank, Google selects an ad from various bids to show as a result for the relevant keyword searches.
The exact auction system for Google PPC ads can be complicated, but essentially the better, more targeted your ads are, the more clicks you can get to your website at a cheaper cost. Since Google directs so much web traffic, creating high quality Google PPC ads can be an extremely lucrative marketing technique.
How to Improve PPC Campaigns
There are a few main factors that influence PPC ad campaigns, their CPC, and how relevant and effective they can be. Better pay-per-click campaigns will improve your overall ROI and more specifically ROAS – return on ad spend. To help improve pay-per-click-ads, improve upon keywords and landing pages to create better PPC campaigns.
PPC Keywords
Finding the right keywords is vital to an effective PPC campaign. Since most PPC ads are shown as search engine results, you’ll need to pick the most relevant keywords for your ads to appear under. Your list of PPC keywords should include long-tail variations, and both low and high search volume keywords, including of course the most relevant keywords to your ad.
Use relevant keywords that best match your ad and the product or services you are advertising. Your list of keywords should be long, including all of the long-tail infrequently searched terms as well so that you exhaust every possible relevant keyword. Check up on PPC campaigns, update keywords, and refine lists so that you keep the keywords as up to date and as relevant as possible.
You can also add negative keywords – keywords you explicitly don’t want your ads to appear for. If there are related keywords that are close but not actually related to your brand, or keywords that do not convert well (like phrases including the word “free”) you can select against those keywords to keep your list relevant and reduce wasted clicks.
Landing Page Optimization
Optimize landing pages for each ad so that you can specifically appeal to users who clicked on that ad. Use CRO (conversion rate optimization) techniques on your landing pages to ensure that you convert as many possible visitors into leads or customers. Test for the best possible copy, creative, and format on your landing pages, and make sure your calls to action are clear and concise.
Landing pages are important to PPC because they factor into Google Ads’ Quality Score, so creating a good landing page is important not only to improve conversions, but to lower CPC and improve quality score.
Create Focused, Quality Ads
Ultimately, your PPC campaigns will be successful if you create quality ads with focused targeting. Consider your target customer personas and create ads that you think would appeal the them. The higher the quality of the ad, along with focused audience targeting, the higher your Google Quality Score will be, lowering CPC.
Create great ads to see great results, and keep updating and checking in on your ads to ensure that they are performing well and bringing in leads and conversions.



Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.